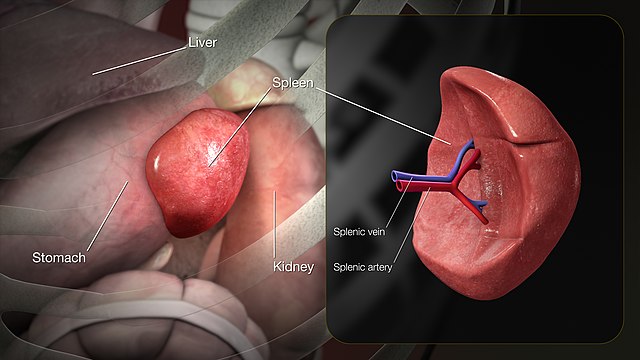
Can you live without a spleen? The spleen serves many functions, but you can live without it. Having it removed will affect your life, though. Your spleen is just inside your left rib cage, above your stomach. It is about 12 cm long and weighs approximately 70 g, about the size of an avocado.
So, what does the spleen do? The spleen has five main jobs. First, it filters the blood. The spleen removes old and broken red blood cells from the blood circulation. It has a filter that is made of narrow passages. Healthy red blood cells can pass through very easily, but damaged cells get caught. When they are stuck, they are broken down by macrophages, which are white blood cells, then removed from the body.
Second, it stores blood. The blood vessels in the spleen are able to get wider, allowing blood to pool in the spleen. The average spleen can hold up to a cup of blood. If you suddenly need more blood, the spleen can release the blood back into circulation.
Third, the spleen stores iron it removes from the red blood cells it breaks down. This iron is stored in the spleen before being passed to the bone marrow so that it can be used to make more red blood cells.
Fourth, the spleen detects and attacks invading organisms in the body. The spleen can detect invading microorganisms as they pass around in the blood. When it detects an invader, the spleen and the lymph nodes start to produce lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell. Lymphocytes can produce antibodies to the virus or organism that has invaded and kill it. Antibodies are proteins that are created in response to a specific virus or bacteria and they can kill the microorganism. A new antibody is made for every new organism and there is no limit to how many antibodies can be made. The white blood cells can also trap invading organisms, preventing them from spreading through the body.
Fifth, the spleen, along with the rest of the lymphatic system, works to keep the fluid level in the body the same. We have a watery fluid that flows around our lymphatic system, called lymph. This fluid starts as plasma in the blood. When blood passes through veins and capillaries, the plasma leaks into the tissue and spaces around the cells. It carries oxygen, nutrients, and proteins to cells. On the way back, it picks up bacteria, viruses, and other harmful organisms or damaged cells. This fluid can’t stay in the tissue and the lymphatic system and the spleen are responsible for keeping an eye on it and making sure what goes in and what comes out balances. The lymph is filtered and then fed back into the blood.
There is one extra thing the spleen does, but it does it more for some people than for others. When the spleen stores blood, it stores oxygenated blood. If the body is low on oxygen, the spleen can put that oxygenated blood back into the blood stream and provide a source of oxygen. Researchers have looked at tribes of people that dive deep underwater in the hunt for fish or pearls and they have found that their spleens are usually about 50% larger than people that don’t dive. The Bajau people are a good example. This oxygenated blood that the spleen stores might be the reason why the Bajau people are able to stay underwater for minutes at a time.
There are several reasons why a spleen might need to be removed. They filter out the damaged red blood cells, but they can go wrong and filter out normal red blood cells as well. This can cause anemia. They can stop producing enough white blood cells or they can become swollen with too much fluid. In severe circumstances, the spleen can actually rupture, which is a life threatening injury because the blood that passes through the spleen will just leak into the body.
So, if the spleen is that important, how can we live without a spleen? The work the spleen does to filter your blood will be taken up by the liver. The rest of the lymphatic system can produce white blood cells, antibodies, and regulate the lymph fluid in the body, but they will not be quite as effective as having a spleen. People with no spleen are more susceptible to infection and they are recommended to take low level antibiotics for the rest of their life. They might not be able to fight off a bacterial infection and the antibiotics can take care of that. They also need to make sure they have had all necessary vaccinations. However, if they are careful, there is no reason that someone can’t live without a spleen. And this is what I learned today.
Image By https://www.scientificanimations.com – https://www.scientificanimations.com/wiki-images, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=91085787
Sources
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/spleen-problems-and-spleen-removal/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21567-spleen
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17829-enlarged-spleen
https://www.chp.edu/our-services/transplant/liver/education/organs/spleen-information
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antibody
https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/spleen.html
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/25209-lymph
https://news.berkeley.edu/2018/04/19/enlarged-spleen-key-to-diving-endurance-of-sea-nomads
